Introduction
Lighting plays a crucial role in enhancing the ambiance and functionality of any space. However, achieving the perfect lighting effect often requires more than just installing light sources. That’s where diffusers come into play. Diffusers are essential components in lighting fixtures that help to control the distribution and quality of light. In this blog, we’ll explore the different types of diffusers and their wide-ranging applications across various industries.
Types of Diffusers
Frosted Diffusers
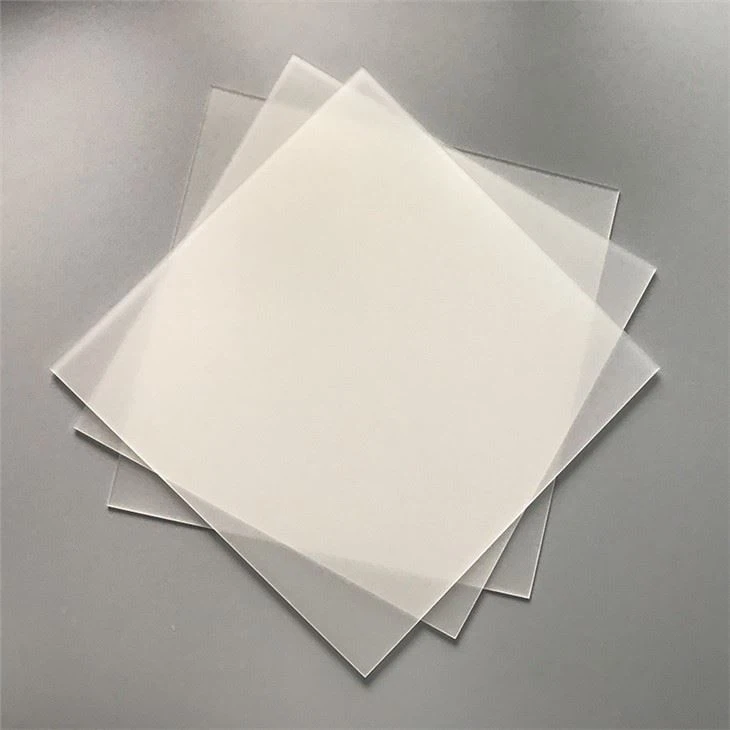 Frosted diffusers feature a textured surface that scatters light, creating a soft and uniform illumination. They are commonly used in LED panel lights, ceiling fixtures, signage, and displays to enhance visual comfort and aesthetics.
Frosted diffusers feature a textured surface that scatters light, creating a soft and uniform illumination. They are commonly used in LED panel lights, ceiling fixtures, signage, and displays to enhance visual comfort and aesthetics.
Prismatic Diffusers
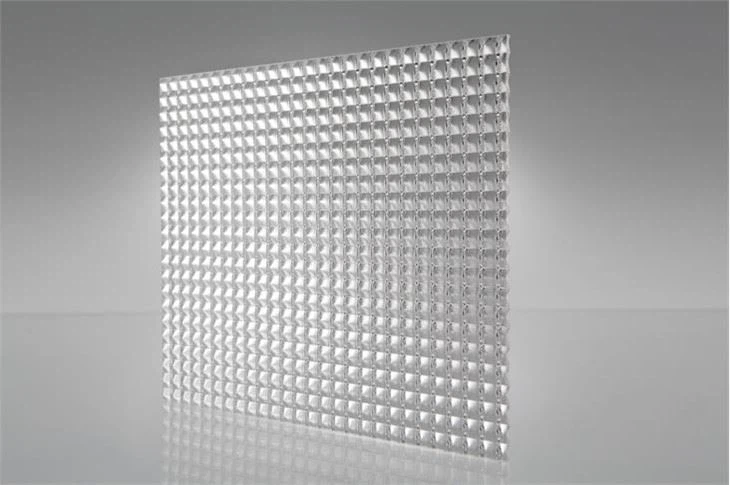 Prismatic diffusers have small prisms on one side, which help to direct and diffuse light. They are effective in controlling glare and distributing light evenly, making them ideal for lighting fixtures in offices, schools, and commercial buildings.
Prismatic diffusers have small prisms on one side, which help to direct and diffuse light. They are effective in controlling glare and distributing light evenly, making them ideal for lighting fixtures in offices, schools, and commercial buildings.
Lenticular Diffusers
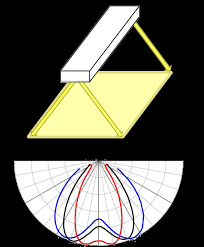 Lenticular diffusers consist of elongated convex lenses that spread light in a specific direction. They are suitable for applications requiring precise light control, such as automotive lighting, photography, and medical devices.
Lenticular diffusers consist of elongated convex lenses that spread light in a specific direction. They are suitable for applications requiring precise light control, such as automotive lighting, photography, and medical devices.
Micro-Prismatic Diffusers
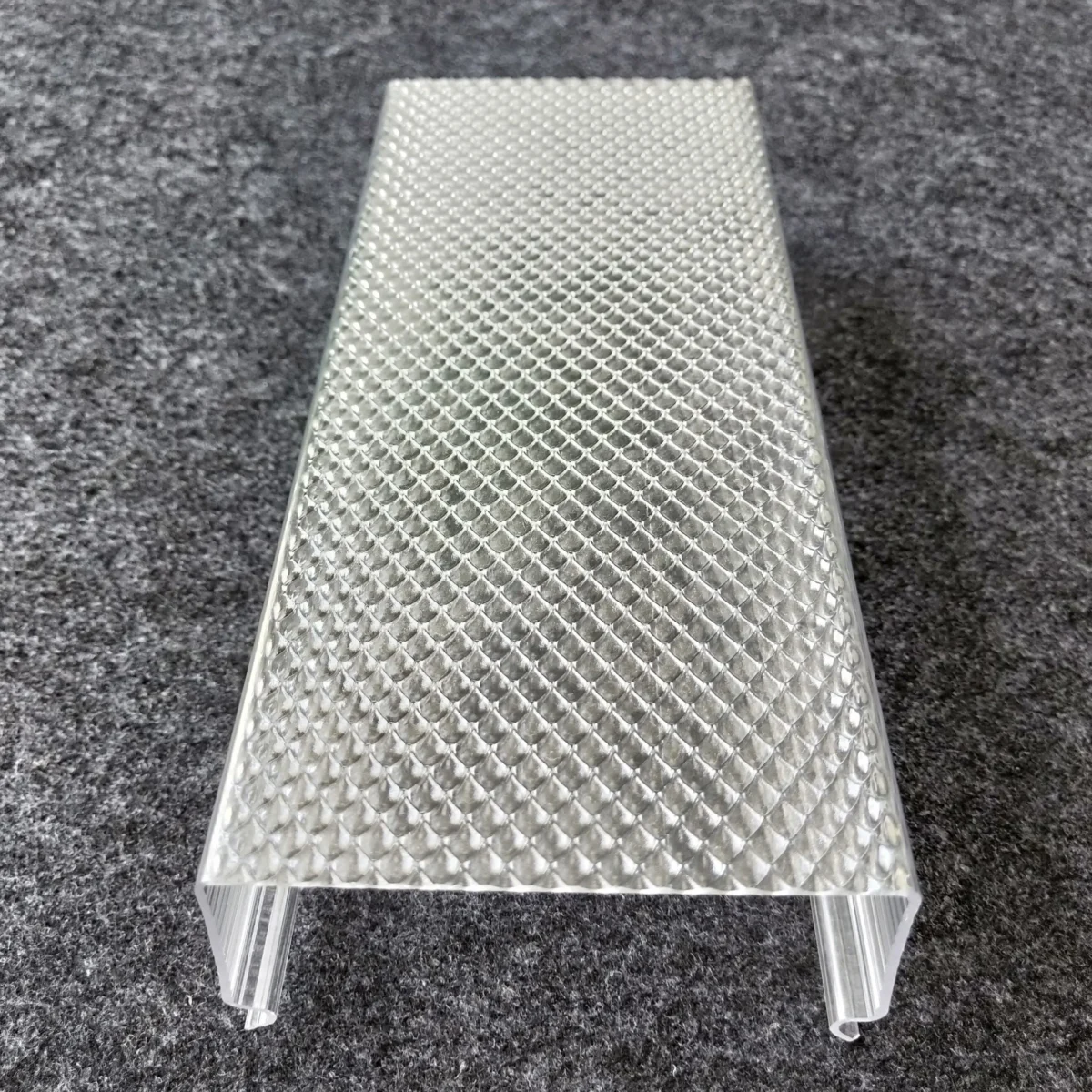 Micro-prismatic diffusers feature tightly spaced prisms that provide excellent light diffusion while minimizing glare. They are commonly used in office lighting to ensure visual comfort for occupants.
Micro-prismatic diffusers feature tightly spaced prisms that provide excellent light diffusion while minimizing glare. They are commonly used in office lighting to ensure visual comfort for occupants.
Opal Diffusers
 Opal diffusers are made from translucent materials with a smooth surface, resulting in a soft and diffused light output. They are popular in decorative lighting fixtures, residential lighting, and retail environments.
Opal diffusers are made from translucent materials with a smooth surface, resulting in a soft and diffused light output. They are popular in decorative lighting fixtures, residential lighting, and retail environments.
Honeycomb Diffusers
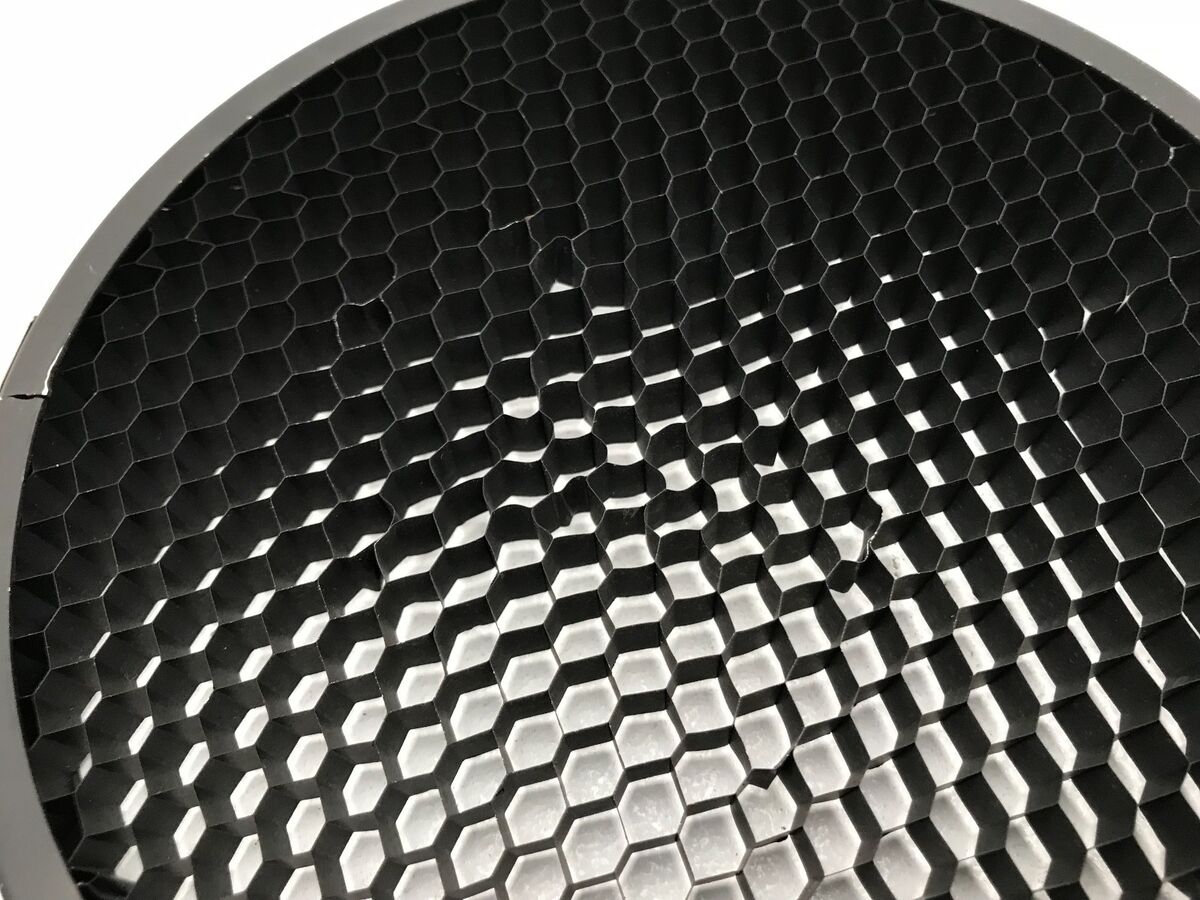 Honeycomb diffusers consist of a grid of hexagonal cells that control the direction of light and reduce glare. They find applications in architectural lighting, photography, and display lighting.
Honeycomb diffusers consist of a grid of hexagonal cells that control the direction of light and reduce glare. They find applications in architectural lighting, photography, and display lighting.
Applications of Diffusers
- Architectural Lighting: Diffusers play a vital role in architectural lighting by softening and distributing light to create inviting and comfortable spaces. They are commonly used in downlights, wall sconces, and pendant fixtures in residential, commercial, and hospitality settings.
- Retail Lighting: In retail environments, diffusers help to enhance product visibility and create an appealing shopping experience. They are used in track lighting, shelf lighting, and display cases to accentuate merchandise while minimizing glare.
- Medical Lighting: Diffusers are essential in medical lighting applications where precise illumination is required for examinations, surgeries, and patient care. They help to reduce eye strain and provide uniform lighting for accurate diagnostics.
- Automotive Lighting: Automotive diffusers are used in headlights, taillights, and interior lighting to control the direction and intensity of light. They improve visibility for drivers while enhancing the aesthetics of vehicles.
- Photography and Film: Diffusers are indispensable tools in photography and film production for creating soft, flattering lighting effects. They are used with studio lights, flash units, and LED panels to diffuse harsh light and eliminate shadows.
Selection of right Diffuser
- Light Transmission (Transmittance): This parameter measures the percentage of light that passes through the diffuser material. Higher light transmission indicates better efficiency in transmitting light and is essential for maintaining brightness levels in the illuminated space.
- Diffusion Efficiency: Diffusion efficiency refers to the diffuser’s ability to scatter light evenly across its surface. A diffuser with high diffusion efficiency ensures uniform illumination, minimizing hotspots and shadows.
- Glare Reduction: Glare is caused by excessive brightness or contrast in the field of view, leading to discomfort and reduced visibility. The diffuser’s design and surface properties influence its ability to reduce glare by scattering and diffusing light rays effectively.
- UV Resistance: Some lighting applications, especially those exposed to sunlight or UV radiation, require diffusers with UV-resistant properties. UV-resistant diffusers prevent yellowing, degradation, and loss of optical clarity over time.
- Temperature Resistance: Diffusers must withstand the operating temperatures of the lighting fixture and environment without warping, melting, or deforming. Temperature resistance ensures long-term durability and performance in various conditions.
- Material Compatibility: The diffuser material should be compatible with the light source and the intended application. Common diffuser materials include acrylic, polycarbonate, glass, and polyester, each offering different optical and mechanical properties.
- Color Rendering Index (CRI): The CRI measures the ability of a light source to accurately render colors compared to a natural light source. Some diffusers may affect the CRI of the light passing through them, so it’s essential to consider how the diffuser material may impact color rendition in your application.
- Light Distribution Pattern: Different diffusers have varying patterns for distributing light, such as wide-angle or narrow-angle distribution. Choose a diffuser with a distribution pattern that suits the specific lighting needs of your application, whether it’s for general illumination or highlighting specific areas.
- Optical Efficiency: Optical efficiency refers to the diffuser’s ability to efficiently transmit and distribute light while minimizing light loss through absorption or reflection. High optical efficiency ensures maximum utilization of light output from the source.
- Impact Resistance: Depending on the application, such as in high-traffic areas or industrial settings, diffusers may be subject to impacts or rough handling. Choose diffusers with high impact resistance to withstand physical damage and maintain optical clarity.
- Compatibility with Light Source: Ensure that the diffuser material and design are compatible with the specific type of light source you’re using, whether it’s LEDs, fluorescent lamps, or incandescent bulbs. Compatibility ensures optimal performance and longevity of both the diffuser and the light source.
Conclusion
Diffusers are versatile components that play a critical role in shaping the quality and distribution of light across various applications. Whether in architectural lighting, retail environments, medical facilities, automotive design, or photography, diffusers help to enhance visual comfort, improve aesthetics, and optimize functionality. Understanding the different types of diffusers and their applications is essential for designing lighting solutions that meet the specific needs of each environment.
Also Read: Understanding Operational Amplifiers: The Basics and Beyond